“There are situations in the emergency department when intravenous access procedures fail or are insufficient to meet the clinical needs of the patient. Alternative access methods must be available under such circumstances and their usage should be a part of the emergency medicine practice privileges. These alternate access modalities include, but are not limited to, intraosseous lines.”1


- Overview
- Features
- Recommendations
- Products & Accessories
- EIFU & Resources
Our commitment to safety and quality
BD® Intraosseous Vascular Access System products evolve to meet the highest standards of quality and reliability.
Reliable IO access, when every second counts
Every day, you make decisions that save lives. In the most chaotic moments when every second matters, you know exactly what your patient needs and the best course of treatment.
When intraosseous access (IO) is the best option for vascular access, clinicians and emergency care professionals rely on the BD® Intraosseous Vascular Access System—the confident choice for delivering fluids and medications safely during critical resuscitations and life-saving procedures.
With innovations designed to deliver safety, reliability and performance, the BD® Intraosseous Vascular Access System gives you enhanced control and a safety feature designed to protect against needlestick injuries.
Elevating IO Access:
Safety. Reliability. Performance.
We've evolved IO access so you can choose the right tool, each time, in every emergent scenario. Whether you prefer manual or powered IO, each component of the BD® Intraosseous Vascular Access System is designed to help you perform in any emergency scenario in the ED or EMS environment.
Why the BD® Intraosseous Vascular Access System stands apart

Integrated safety needle
The only IO needles designed to protect against needlestick injuries with integrated passive needle tip safety

Comprehensive needle set
With five needle lengths, you can feel confident you have the length you need to safely achieve access in patients of all sizes, from neonates to the largest patients

Multi-light battery indicator
The only IO powered driver featuring a multi-light battery indicator for instant battery charge status identification—so you know it’s ready to perform when you need it

Enables stabilization
The only IO securement device designed to enable stabilization of the IO device on the contours of any relevant anatomy and can be placed either before or after the extension set

Rechargeable battery
The only IO powered driver with a rechargeable battery that lasts up to 12× longer than the non-rechargeable Teleflex EZ-IO®1*
*Based on bench testing and may not necessarily be indicative of clinical performance

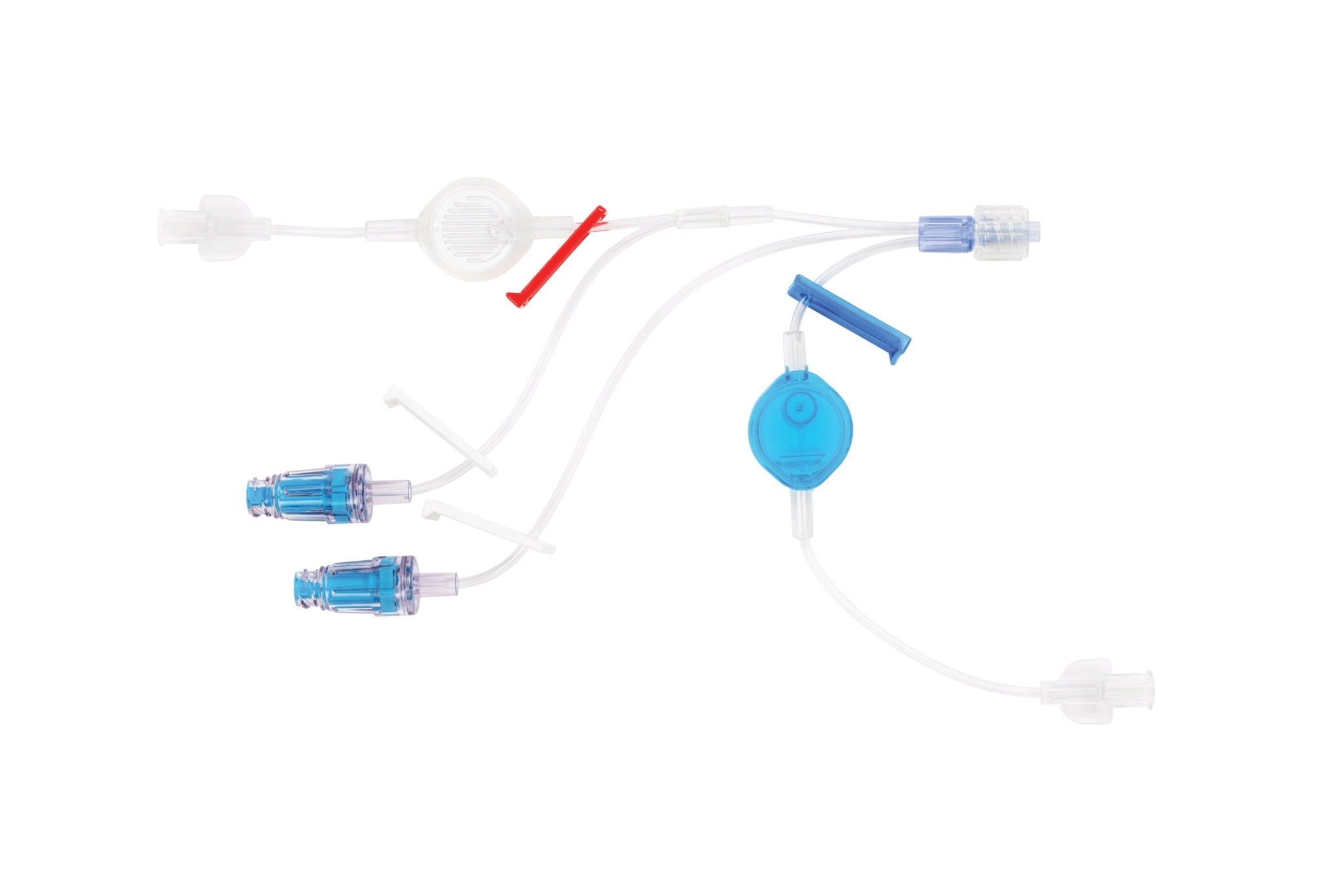
Extension Set
Provides access for continuous infusions and is easily disinfected in just 3 seconds with an alcohol swab
Patient and provider safety is our top priority
Minimize risk of needlestick injuries
Needlestick injuries pose a constant safety threat to healthcare providers, causing fear, anxiety and emotional stress in workers2,3 and financial strain on hospitals.2
On average, each exposure costs a hospital up to $3,7762
BD® Intraosseous Needles are the only IO needles that feature an integrated passive needle tip safety designed to protect against needlestick injuries—helping to protect healthcare workers from inadvertent needlesticks in emergent settings.
- Aligned with INS standards recommending passive safety-engineered devices for the prevention of needlestick injuries4
- Meets ISO standards and FDA guidance for sharps prevention5,6
- Integrated passive needle tip safety feature available on all five needle sizes
Safe IO access insertions
Unsuccessful insertions increase treatment delays, reduce patient satisfaction and significantly increase risk of complications.7 Difficult venous access (DVA) is reported to affect over 33% of hospitalized adults and up to 50% of hospitalized children who require a PIVC, making first-attempt success harder to achieve.8
The BD® Intraosseous Powered Driver is designed with innovations to safely accommodate insertions for all patients:
-
Enables IO access for adult and pediatric patients when IV access is difficult or impossible to obtain in emergent, urgent or medically necessary cases for up to 24 hours
-
Rechargeable battery lasts up to 12x longer than the non-rechargeable Teleflex EZ-IO®1*
-
Securement device prevents IO cannula dislodgement
Perform IO access with confidence, anytime
Reliable performance every time
IO access is a reliable bridging method for gaining vascular access for in-hospital adult emergency patients under trauma or medical resuscitation with impossible peripheral IV access.9
The BD® Intraosseous Vascular Access System delivers high-quality, reliable performance you can count on:
-
Long-lasting rechargeable battery with 12× more life than the non-rechargeable Teleflex EZ-IO®1*
-
Powered driver stops immediately upon releasing the trigger
Ready when seconds count
In ED and EMS settings, life-saving decisions must be made in seconds. The BD® Intraosseous Vascular Access System is designed with multiple visual indicators, so you can be confident that the device is powered and ready when you need it:
-
Easy Micro-USB recharging
-
Multi-light battery indicator provides instant charge status visibility
Elevate IO access comfort and efficiency
Increased control, in your hands
Ergonomics and ease of use are critical factors impacting control and efficiency in clinical procedures.
The BD® Intraosseous Vascular Access System is an easy-to-use device with innovations designed to improve the user experience:
-
BD® Intraosseous Powered Driver is ergonomically designed for user comfort
-
Accommodates larger hands more comfortably
-
BD® Intraosseous Manual Driver's ergonomic handle increases controlled insertion into the vascular space
-
Securement device's snap-on feature allows it to be placed independently of the extension set, eliminating the need to disconnect and reconnect the extension set
Expert training for proficiency
Our clinical experts are here to support your success with the BD® Intraosseous Vascular Access System. Leverage their expertise and tools like the IO Competency Checklist, in-service training, and learning sessions to safely upgrade your facility or enhance your IO access technique and proficiency.
Please consult product labels and inserts for any indications, contraindications, hazards, warnings, precautions and directions for use.
- Internal file at BD (M661-048.0 dated 10/15/2019).
- Lee J, Botteman M, Nicklasson L. A Systematic Review of the Economic and Humanistic Burden of Needlestick Injury in the United States. Am J Infect Control. 2004;32(3):E43. doi: 10.1016/j.ajic.2004.04.064.
- Green B, Griffiths EC. Psychiatric consequences of needlestick injury. Occup Med (Lond). 2013;63(3):183-188. doi:10.1093/occmed/kqt006.
- Nickel B, Gorski L, Kleidon T, et al. Infusion Therapy Standards of Practice, 9th Edition. J Infus Nurs. 2024;47(1S Suppl 1):S1-S285. doi:10.1097/NAN.0000000000000532.
- IO Needle Patent.
- ISO Standard 23908.
- Kusminsky RE. Complications of central venous catheterization. J Am Coll Surg. 2007;204(4):681–696. doi: 10.1016/j.jamcollsurg.2007.01.039.
- Sou V, McManus C, Mifflin N, Frost SA, Ale J, Alexandrou E. A clinical pathway for the management of difficult venous access. BMC Nurs. 2017;16:1–7. doi: 10.1186/ s12912-017-0261-z 2018.
- Leidel BA, Kirchhoff C, Bogner V, et al. Is the intraosseous access route fast and efficacious compared to conventional central venous catheterization in adult patients under resuscitation in the emergency department? A prospective observational pilot study. Patient Saf Surg. 2009;3(1):24. doi: 10.1186/1754-9493-3-24.
BD-136077 (09/24)
Take a closer look at the evolution of IO access
Discover an IO system that helps elevate safety, reliability, and performance in emergencies.

- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
Patented, integrated passive stylet tip
Designed to protect healthcare providers from inadvertent needlesticks in emergent situations—the only IO needles with this feature
Color-coded needle packaging
Quickly communicates needle length
Comprehensive selection of five stainless steel needles (15mm, 25mm, 35mm, 45mm, 55mm)
From neonates to the largest patients, you can feel confident you have the length you need to achieve access
Multi-light battery indicator
Provides instant identification of battery charge status, so you can be confident that the powered driver is ready to perform
Powered driver
Provides instant action that stops immediately upon releasing the trigger
Ergonomic design
Features longer handle than Teleflex EZ-IO™, accommodating larger hands more comfortably
Rechargeable battery
Lasts up to 12x longer than the non-rechargeable Teleflex EZ-IO™1*
BD® Intraosseous Vascular Access System accessories

- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
Unique contoured shape
Designed to provide stabilization on the contours of any relevant anatomy.
Packaged with the needle set or manual driver kit
Eliminates the hassle of having to reach for a separate stabilization device
Can be placed either before or after the extension set
Helping to minimize procedure steps
BD MaxZero™ Needle-free Connector
Provides access for continuous infusions and is easily disinfected in just 3 seconds with an alcohol swab
BD Max™ T-Connector
Provides an additional access point for use in emergent situations, enabling continuous infusions of critical medications
Please consult product labels and inserts for any indications, contraindications, hazards, warnings, precautions and directions for use.
- Internal file at BD (M661-048.0 dated 10/15/2019)
BD-136077 (09/24)
Follow the leaders: Achieve IO access proficiency
Multiple professional industry associations recommend IO access for situations where care is compromised without rapid vascular access and IV access is not available. These include:
- American College of Emergency Physicians (ACEP)1
- Emergency Nurses Association (ENA)2
- American Heart Association (AHA)3
- Infusion Nurses Society (INS)4
- National Association of EMS Physicians (NAEMSP)5,6
“IO access has a reported high rate of first-time insertion success with low complications and reduced vascular access insertion attempts. [...] Use the IO route in the event of a cardiac arrest if intravenous (IV) access is not available or cannot be obtained promptly. Pediatric advanced life support guidelines recommend the use of the IO route as an initial vascular access route in case of cardiac arrest or if intravenous access cannot be obtained within 30 seconds.”4
“IO access may be appropriate for primary vascular access in select cases.1,4 In out-of-hospital environments, IO access may provide significant time savings that could benefit patients in emergent situations by decreasing the time required to achieve access and the time required to administer the necessary fluids and medications.”6
IO access proficiency starts here
Access BD® Intraosseous Vascular Access System product overview videos, instructions for use and more.
This is a modal window.
Beginning of dialog window. Escape will cancel and close the window.
End of dialog window.
This is a modal window. This modal can be closed by pressing the Escape key or activating the close button.
BD® Intraosseous Powered Driver Animation
Your 24/7 clinical support partner
Our Medical Information (MI) team of scientists and nurses is here to help 24/7/365. Contact us any time via phone (1-800-555-7422) or email (medical.services@bd.com) for answers to your technical or clinical questions about BD products and procedures in which they are used.
Please consult product labels and inserts for any indications, contraindications, hazards, warnings, precautions and directions for use.
- Alternative Methods to Vascular Access in the Emergency Department. American College of Emergency Physicians (ACEP) website. https://www.acep.org/patient-care/policy-statements/alternative-methods-to-vascular-access-in-the-emergency-department/. Published June 2011. Revised January 2017. Accessed March 31, 2021.
- Position Statement - The Role of the Registered Nurse in the Use of Intraosseous Vascular Access Devices. Emergency Nurses Association (ENA) website. http://www.ena.org/docs/default-source/resource-library/practice-resources/position-statements/joint-statements/roleofrnininsertionof-ioaccessdevicepositionpaper.pdf?sfvrsn=e5f8b8f9_16. Published December 2019. Accessed May 27, 2021.
- Kleinman ME, Chameides L, Schexnayder SM, et al. Part 14: Pediatric Advanced Life Support. 2010 American Heart Association Guidelines for Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation and Emergency Cardiovascular Care. 2010;122(3):S876–S908.
- Nickel B, Gorski L, Kleidon T, et al. Infusion Therapy Standards of Practice, 9th Edition. J Infus Nurs. 2024;47(1S Suppl 1):S1-S285. doi:10.1097/NAN.0000000000000532.
- Fowler R, Gallagher JV, Isaacs SM, Ossman E, Pepe P, Wayne M. The role of intraosseous vascular access in the out-of-hospital environment (Resource document to NAEMSP Position Statement). Prehosp Emerg Care. 2007;11(1):63–66. doi: 10.1080/10903120601021036.
- O'Connor RE. Intraosseous Vascular Access in the Out-of-Hospital Setting Position Statement of the National Association of EMS Physicians. Prehosp Emerg Care. 2007;11(1):62. doi: 110.1080/10903120601020939.
BD-136077 (09/24)