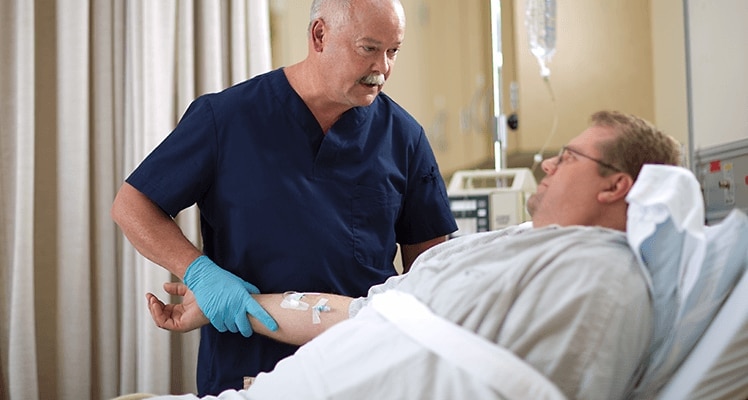
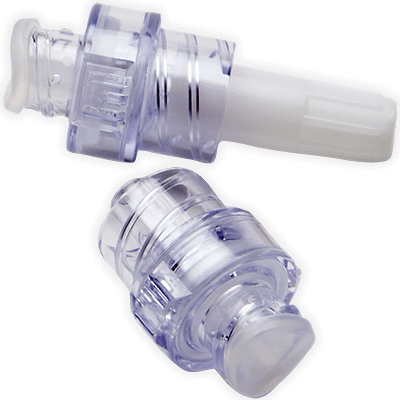
La valve bidirectionnelle BD Q-Syte™ a une conception à septum fendu qui adhère aux directives relatives à la réduction des taux d’infection du flux sanguin liée au cathéter (CRBSI) établies par les Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) et l’International Nosocomial Infection Control Consortium (INICC).
Valve bidirectionnelle BD Q-Syte™
Protégez vos cliniciens avec la conception à septum fendu conforme aux directives établies par le CDC et l’INICC

- Présentation
- Mode d’emploi électronique et ressources
- Rupp ME, Sholtz LA, Jourdan DR, et al. Outbreak of bloodstream infection temporally associated with the use of an intravascular needleless valve. Clin Infect Dis. 2007;44 : 1408-1414.
- Salgado CD, Chinnes L, Paczesny TH, Cantey JR. Increased rate of catheter-related bloodstream infection associated with use of a needleless mechanical valve device at a long-term acute care hospital. Infect Control Hosp Epidemiol. 2007;28 : 684-688.4.
Le corpus de publications de BD sur le secteur et nos offres vous donnent des informations que vous pouvez utiliser pour continuer à viser l’excellence.
BD met à votre disposition des ressources de formation pour vous aider à améliorer vos pratiques cliniques, dans le cadre de notre objectif « faire progresser le monde de la santé ».
BD soutient le secteur des soins de santé en proposant des produits et des services de pointe pour améliorer les soins tout en diminuant les coûts. Nous organisons des événements et participons à des rencontres qui excellent à faire progresser le monde de la santé, conformément à notre devise « faire avancer le monde de la santé™ ».
BD promeut l’excellence clinique en fournissant diverses ressources sur les bonnes pratiques, les innovations cliniques et les tendances du secteur de la santé.